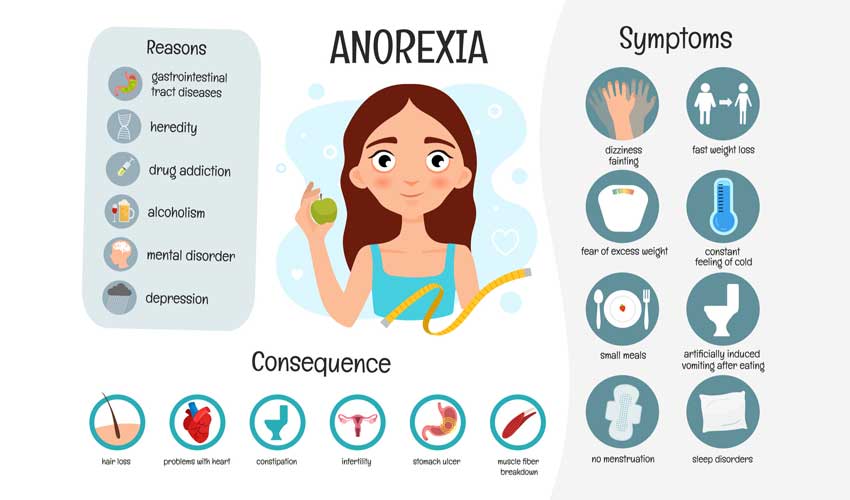
Emotional and behavioral signs and symptoms may include:
Anorexia (an-o-REK-see-uh) nervosa — often simply called anorexia — is an eating disorder characterized by an abnormally low body weight, an intense fear of gaining weight and a distorted perception of weight.
Physical signs and symptoms of anorexia may include:
Behavioral symptoms of anorexia may include attempts to lose weight by:

Emotional and behavioral signs and symptoms may include:
Unfortunately, many people with anorexia don't want treatment, at least initially. Their desire to remain thin overrides concerns about their health. If you have a loved one you're worried about, urge her or him to talk to a doctor.
If you're experiencing any of the problems listed above, or if you think you may have an eating disorder, get help. If you're hiding your anorexia from loved ones, try to find a person you trust to talk to about what's going on.
There's no guaranteed way to prevent anorexia nervosa. Primary care physicians (pediatricians, family physicians and internists) may be in a good position to identify early indicators of anorexia and prevent the development of full-blown illness. For instance, they can ask questions about eating habits and satisfaction with appearance during routine medical appointments.
If you notice that a family member or friend has low self-esteem, severe dieting habits and dissatisfaction with appearance, consider talking to him or her about these issues. Although you may not be able to prevent an eating disorder from developing, you can talk about healthier behavior or treatment options.